Organizational environment
Companies in different geographies have witnessed 50 years of permanent change from
all areas through industrialization, systematization, regionalization and now we are facing
the revolution generated by the different behaviors of the generations that co-inhabit the
interior of organizations, and having clear that now part of the differentiation is achieved
through the Human Resource in each organization.
In companies in the services sector, this differentiation is stronger, given that the product
itself is the service they provide with opportunity, quality and providing added value to
their customers.
We are thus witnessing the presence of 4 generations interacting in organizations such as:
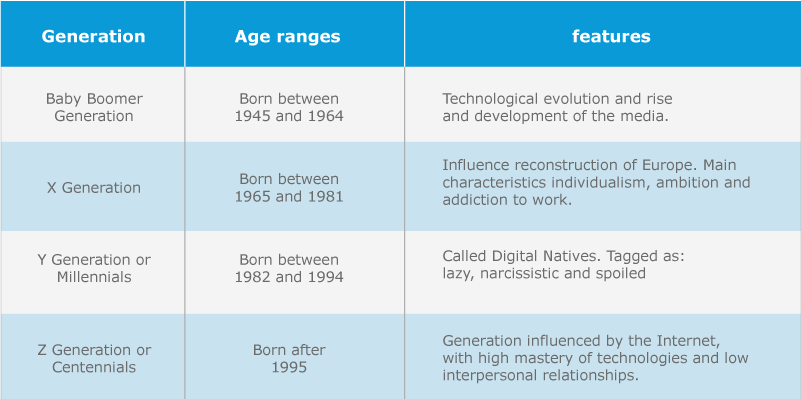
Organizational competencies and characteristics of each generation.
From the business point of view, the characteristics that govern each of the 4 generations
are the following:
1. Baby Boomer Generation.
Being a generation framed by optimism by virtue of the end of the Second World
War, and the exponential growth of the birth rate as a consequence of the same
optimism, this generation is governed by job and family stability. The fundamental
characteristics from the business field are the sense of belonging, and the work
balance with high levels of productivity and development in its learning curve and
implementation of career plans generating low turnover in organizations.
2. X Generation
Generation X is governed by the achievement of work and high productivity as a
philosophy of life, where getting and keeping a job was their great challenge.
However, this fundamental purpose led them to be very individualistic, without a
vocation for teamwork and with values of ambition and addiction to work
(workaholic).
3. Y Generation or Millennials
Generation Y is influenced by Technology. Although they were not born in the
digital world but analog, they are 100% immersed in the day to day to carry all
their activities from a screen (laptop, Tablet or smartphones). As a result of the
regional and global economic crises, they have been forced to have a greater
academic preparation to be able to apply for a job, with increasing levels of
competition that has led them to fight for the first positions, the high
representation through leadership, but from the approach of the first Me, second
Me and third Me (Time Magazine 2014).
4. Z Generation or Centennials.
This generation is influenced by the Internet and social and work networks. They
have a sense of immediacy both in the pursuit of their accomplishments and in
their lifestyle. Among its characteristics is a low sense of belonging, multi-tasking,
but with a high level of dispersion and a short attention span. They are called to fill
the new jobs as influencers and all the new roles that are under construction or do
not yet exist. They are very critical and highly demanding consumers.
Cohesion of work teams – The great challenge
Given that, for organizations, their competitors are not only local but also regional and
global, and also that their customers and market niches are increasingly demanding and
not very loyal, it requires them to harmonize work teams to obtain the best returns, a
stable market and growing aggregate values.
Obtaining increases in market share is governed by the adoption of new digital and virtual
service channels, as well as immediate response times and customer profiling through the
proper use of big data.
All of the above must be governed by an adequate interaction of the work teams where
the 4 generations mentioned are immersed with different levels of knowledge, skills and
expectations. The question then is how to manage such a diverse and disparate
contingent in terms of training, experience, lifestyles and expectations for the future?
Organizations have made many adjustments to achieve that goal and we emphasize the
main ones:
1. Levels of training and career and succession plans. The organizations have
established career plans and their human resources areas have implemented the
closing of gaps between required and current competencies of their collaborators,
as well as the recognition of the performance and achievements of each
collaborator.
2. Adoption of flexible and variable models in its remuneration schemes, offering
portfolios that serve all its collaborators according to their tastes, habits and
projections, seeking to generate better organizational climates, reduction of
turnover and improvement of productivity.
3. Redefinition of culture and climate models, seeking to generate greater
participation at all organizational levels, empowering all areas through agile
methodologies that reward the achievement of new products and innovation from
productive areas and base levels.
The challenge is understood and the methodologies are underway. The important thing is
to recognize that there are no magic formulas and although good market practices must
be taken into account, each organization has its own reality and different growth spaces.
Carlos Mosquera Franco
RPT Consultants
